Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小山 元道*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; 澤口 孝宏*; Yang, Z.*; 北條 智彦*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
鉄と鋼, 110(3), p.197 - 204, 2024/02
被引用回数:0The local plasticity and associated microstructure evolution in Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium-Mn steel (wt.%) were investigated in this study. Specifically, the micro-deformation mechanism during L ders banding was characterized based on multi-scale electron backscatter diffraction measurements and electron channeling contrast imaging. Similar to other medium-Mn steels, the Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel showed discontinuous macroscopic deformation, preferential plastic deformation in austenite, and deformation-induced martensitic transformation during L
ders banding was characterized based on multi-scale electron backscatter diffraction measurements and electron channeling contrast imaging. Similar to other medium-Mn steels, the Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel showed discontinuous macroscopic deformation, preferential plastic deformation in austenite, and deformation-induced martensitic transformation during L ders deformation. Hexagonal close-packed martensite was also observed as an intermediate phase. Furthermore, an in-situ neutron diffraction experiment revealed that the pre-existing body- centered cubic phase, which was mainly ferrite, was a minor deformation path, although ferrite was the major constituent phase.
ders deformation. Hexagonal close-packed martensite was also observed as an intermediate phase. Furthermore, an in-situ neutron diffraction experiment revealed that the pre-existing body- centered cubic phase, which was mainly ferrite, was a minor deformation path, although ferrite was the major constituent phase.
小山 元道*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Yang, Z.*; Varanasi, R. S.*; 北條 智彦*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
鉄と鋼, 110(3), p.205 - 216, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 deformation experiments with cold-rolled and intercritically annealed Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel were carried out at ambient temperature to characterize the deformation heterogeneity during L
deformation experiments with cold-rolled and intercritically annealed Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel were carried out at ambient temperature to characterize the deformation heterogeneity during L ders band propagation. Deformation band formation, which is a precursor phenomenon of L
ders band propagation. Deformation band formation, which is a precursor phenomenon of L ders band propagation, occurred even in the macroscopically elastic deformation stage. The deformation bands in the L
ders band propagation, occurred even in the macroscopically elastic deformation stage. The deformation bands in the L ders front grew from both the side edges to the center of the specimen. After macroscopic yielding, the thin deformation bands grew via band branching, thickening, multiple band initiation, and their coalescence, the behavior of which was heterogeneous. Thick deformation bands formed irregularly in front of the region where the thin deformation bands were densified. The thin deformation bands were not further densified when the spacing of the bands was below
ders front grew from both the side edges to the center of the specimen. After macroscopic yielding, the thin deformation bands grew via band branching, thickening, multiple band initiation, and their coalescence, the behavior of which was heterogeneous. Thick deformation bands formed irregularly in front of the region where the thin deformation bands were densified. The thin deformation bands were not further densified when the spacing of the bands was below  10
10  m. Instead, the regions between the deformation bands showed a homogeneous plasticity evolution. The growth of the thin deformation bands was discontinuous, which may be due to the presence of ferrite groups in the propagation path of the deformation bands. Based on these observations, a model for discontinuous L
m. Instead, the regions between the deformation bands showed a homogeneous plasticity evolution. The growth of the thin deformation bands was discontinuous, which may be due to the presence of ferrite groups in the propagation path of the deformation bands. Based on these observations, a model for discontinuous L ders band propagation has been proposed.
ders band propagation has been proposed.
興津 貴隆*; 北條 智彦*; 諸岡 聡; 宮本 吾郎*
鉄と鋼, 110(3), p.260 - 267, 2024/02
被引用回数:0We have investigated the dynamic tensile properties of 4, 5, 6-mass%-Mn-containing low carbon steels with multi-phase microstructures containing retained austenite. The five materials used were classified into two groups. The first group of materials, with around 10% of retained austenite, showed normal strain rete dependence of yield strength (YS) and tensile strength (TS) as in conventional high strength steels. The second group of materials, containing 25-36% of retained austenite, exhibited L ders elongation showed also normal strain rate dependence in YS and flow stress at L
ders elongation showed also normal strain rate dependence in YS and flow stress at L ders deformation, but TS varied in a complex manner. Among the second group, in the 4 Mn steel, TS was nearly constant at strain rates below 1 s
ders deformation, but TS varied in a complex manner. Among the second group, in the 4 Mn steel, TS was nearly constant at strain rates below 1 s but increased slightly at higher strain rates. In the 5 and 6 Mn steels, TS once decreased up to the strain rate of 1 or 10 s
but increased slightly at higher strain rates. In the 5 and 6 Mn steels, TS once decreased up to the strain rate of 1 or 10 s , and then began to increase at higher strain rates. These behaviors were discussed in terms of temperature rise during plastic deformation causing suppression of martensitic transformation, and thermal stability of retained austenite. In the 4 Mn steel with relatively unstable retained austenite, almost all the austenite transforms regardless of strain rate. In the 5 and 6 Mn steels, where the retained austenite is moderately stable, strain induced transformation of austenite continues up to high plastic strain, providing a good balance of strength and ductility. At high strain rate, TS decreases slightly due to temperature rise, but at higher strain rates than 1 s
, and then began to increase at higher strain rates. These behaviors were discussed in terms of temperature rise during plastic deformation causing suppression of martensitic transformation, and thermal stability of retained austenite. In the 4 Mn steel with relatively unstable retained austenite, almost all the austenite transforms regardless of strain rate. In the 5 and 6 Mn steels, where the retained austenite is moderately stable, strain induced transformation of austenite continues up to high plastic strain, providing a good balance of strength and ductility. At high strain rate, TS decreases slightly due to temperature rise, but at higher strain rates than 1 s , the strain rate sensitivity of flow stress in ferrite become prominent and the flow stress increases.
, the strain rate sensitivity of flow stress in ferrite become prominent and the flow stress increases.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffraction澤口 孝宏*; 友田 陽*; 吉中 奎貴*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118494_1 - 118494_14, 2023/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:45.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fe-Mn-Si-based alloys, show superior resistance to plastic fatigue compared to the conventional steels, which is ascribed to the reversible back-and-forth movement of Shockley partial dislocations associated with a reversible martensitic transformation between the face-centered cubic  -austenite and hexagonal close-packed
-austenite and hexagonal close-packed  -martensite. The purpose of this study was to gather evidence of the reversible martensitic transformation using in situ neutron diffraction under cyclic loading. Three Fe-30Mn-Si-Al alloys with different Gibbs free energy differences at 298 K were studied to unravel the effect of phase stability on the degree of reversibility.
-martensite. The purpose of this study was to gather evidence of the reversible martensitic transformation using in situ neutron diffraction under cyclic loading. Three Fe-30Mn-Si-Al alloys with different Gibbs free energy differences at 298 K were studied to unravel the effect of phase stability on the degree of reversibility.
 ders band propagation in an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium Mn steel clarified through
ders band propagation in an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium Mn steel clarified through  scanning electron microscopy
scanning electron microscopy小山 元道*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Yang, Z.*; Varanasi, R. S.*; 北條 智彦*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
ISIJ International, 62(10), p.2043 - 2053, 2022/10
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:32.54(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) deformation experiments with cold-rolled and intercritically annealed Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel were carried out at ambient temperature to characterize the deformation heterogeneity during L
deformation experiments with cold-rolled and intercritically annealed Fe-5Mn-0.1C steel were carried out at ambient temperature to characterize the deformation heterogeneity during L ders band propagation. Deformation band formation, which is a precursor phenomenon of L
ders band propagation. Deformation band formation, which is a precursor phenomenon of L ders band propagation, occurred even in the macroscopically elastic deformation stage. The deformation bands in the L
ders band propagation, occurred even in the macroscopically elastic deformation stage. The deformation bands in the L ders front grew from both the side edges to the center of the specimen. After macroscopic yielding, the thin deformation bands grew via band branching, thickening, multiple band initiation, and their coalescence, the behavior of which was heterogeneous. Thick deformation bands formed irregularly in front of the region where the thin deformation bands were densified. The thin deformation bands were not further densified when the spacing of the bands was below
ders front grew from both the side edges to the center of the specimen. After macroscopic yielding, the thin deformation bands grew via band branching, thickening, multiple band initiation, and their coalescence, the behavior of which was heterogeneous. Thick deformation bands formed irregularly in front of the region where the thin deformation bands were densified. The thin deformation bands were not further densified when the spacing of the bands was below  10
10  m. Instead, the regions between the deformation bands showed a homogeneous plasticity evolution. The growth of the thin deformation bands was discontinuous, which may be due to the presence of ferrite groups in the propagation path of the deformation bands. Based on these observations, a model for discontinuous L
m. Instead, the regions between the deformation bands showed a homogeneous plasticity evolution. The growth of the thin deformation bands was discontinuous, which may be due to the presence of ferrite groups in the propagation path of the deformation bands. Based on these observations, a model for discontinuous L ders band propagation has been proposed.
ders band propagation has been proposed.
熊谷 正芳*; 秋田 貢一*; 黒田 雅利*; Harjo, S.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 820, p.141582_1 - 141582_9, 2021/07
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:62.81(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In situ neutron diffraction during 250 cycles of plastic deformation was performed and the diffraction line profile analysis was performed to qualitatively evaluate the change in the microstructure of austenitic stainless steel during the cyclic deformation. The dislocation density increased with increasing number of cycles until 50 cycles but thereafter decreased. The cycle number corresponding to this maximum point differed depending on whether it was evaluated as the total dislocation density or was deconvoluted into edge and screw dislocation densities. At the initial state, edge dislocations were predominant; however, screw dislocations greatly increased at the first stage of cyclic loading. Afterwards, edge dislocations formed cell walls and screw dislocations annihilated.
Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 土田 紀之*; 諸岡 聡; Gong, W.*
ISIJ International, 61(2), p.648 - 656, 2021/02
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:41.35(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) neutron diffraction measurements of two low-alloy steels and a 304-type stainless steel during tensile and creep tests were performed at room temperature. Changes in the diffraction pattern, the integrated peak intensities of austenite (
neutron diffraction measurements of two low-alloy steels and a 304-type stainless steel during tensile and creep tests were performed at room temperature. Changes in the diffraction pattern, the integrated peak intensities of austenite ( ), and the peak positions of
), and the peak positions of  were analyzed and discussed to elucidate the relationship between intergranular stress in
were analyzed and discussed to elucidate the relationship between intergranular stress in  and the occurrence of martensitic transformation during deformation. Tensile loading experiments revealed that the susceptibility to martensitic transformation depended on the
and the occurrence of martensitic transformation during deformation. Tensile loading experiments revealed that the susceptibility to martensitic transformation depended on the  -(hkl) grains, where
-(hkl) grains, where  -(111) grains underwent martensitic transformation at the latest. The
-(111) grains underwent martensitic transformation at the latest. The  -hkl dependence of the susceptibility to martensitic transformation was found to be controlled by the shear stress levels in
-hkl dependence of the susceptibility to martensitic transformation was found to be controlled by the shear stress levels in  -(hkl) grains, which were affected by the intergranular stress partitioning during deformation.
-(hkl) grains, which were affected by the intergranular stress partitioning during deformation.
 -to-
-to- martensitic transformation of biomedical Co-Cr-Mo alloys by introducing parent phase lattice defects
martensitic transformation of biomedical Co-Cr-Mo alloys by introducing parent phase lattice defects森 真奈美*; 山中 謙太*; 佐藤 茂男*; 椿 真貴*; 佐藤 こずえ*; 熊谷 正芳*; 今福 宗行*; 菖蒲 敬久; 千葉 明彦*
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 90, p.523 - 529, 2019/02
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:71.16(Engineering, Biomedical)In this study, we examined the effect of pre-existing dislocation structures in a face-centered cubic gamma-phase on strain-induced martensitic transformation (SIMT) to produce a hexagonal close-packed epsilon-phase in a hot-rolled biomedical Co-Cr-Mo alloy. The as-rolled microstructure was characterized by numerous dislocations as well as stacking faults and deformation twins. SIMT occurred just after macroscopic yielding in tensile deformation. Using synchrotron X-ray diffraction line-profile analysis, we successfully captured the nucleation of epsilon-martensite during tensile deformation in terms of structural evolution in the surrounding gamma-matrix: many dislocations that were introduced into the gamma-matrix during the hot-rolling process were consumed to produce epsilon-martensite, together with strong interactions between dislocations in the gamma-matrix. As a result, the SIMT behavior during tensile deformation was accelerated through the consumption of these lattice defects, and the nucleation sites for the SIMT epsilon-phase transformed into intergranular regions upon hot rolling. Consequently, the hot-rolled Co-Cr-Mo alloy simultaneously exhibited an enhanced strain hardening and a high yield strength. The results of this study suggest the possibility of a novel approach for controlling the  to
to  SIMT behavior, and ultimately, the performance of the alloy in service by manipulating the initial dislocation structures.
SIMT behavior, and ultimately, the performance of the alloy in service by manipulating the initial dislocation structures.
柴田 大受; 角田 淳弥; 馬場 信一; 山地 雅俊*; 石原 正博; 伊与久 達夫; 辻 延昌*
Key Engineering Materials, 297-300, p.728 - 733, 2005/11
熱・機械的特性に優れるセラミックス材料は、高温ガス炉の炉内構造物への適用が期待されている。結晶粒径を微細化した3モル%イットリア含有正方晶ジルコニア多結晶体(3Y-TZP)セラミックスは、高温での超塑性現象を利用した圧延加工が可能であり有望な材料であるが、強度に関するデータは炉内構造物へ適用するために必要な設計基準を作るうえでは十分でない。本研究では、3Y-TZPセラミックスについて、室温で引張り,曲げ,圧縮試験を実施し、得られた強度データに基づき設計基準の概念検討を行った。その結果、平均の引張り強度は曲げ強度よりかなり小さく、応力条件下での正方晶から単斜晶への相変体機構を考慮することが重要であることを示した。また、得られた強度データをWeibull理論により確率論的に検討し、ジルコニア製構造物に対する設計基準の概念を提案した。
星屋 泰二; 江南 和幸*; 山内 清*
Shape Memory Materials and Hydrides (Trans. of Materials Research Soc. Jpn., Vol. 18B), 0, p.1013 - 1016, 1994/00
高温作動型TiPd系形状記憶合金の高温変態特性及び高温変形挙動を明らかにするため、高温電気抵抗測定及び高温引張試験を実施した。その結果、TiPd系合金のマルテンサイト変態開始温度は、第3元素としてCrあるいはFeを添加することによって、800Kから室温まで任意に調整可能であること、また、擬弾性特性を利用すれば、2%までの形状回復歪が利用できることを明らかにした。TiPd系合金は、高い変態温度を有することから、高温用機能材料として有用であるとともに、放射線環境下における耐照射材料として使用できる可能性がある。さらに、原子力分野における同合金の様々の適用例(高温作動型のパイプ継手、フランジ、さらには熱交換器用の止栓プラグ)に関する設計例についても報告する。

 phase in Cu
phase in Cu Al(+Pd) alloy under uniaxial pressure
Al(+Pd) alloy under uniaxial pressure永澤 耿*; 桑原 敦子*; 森井 幸生; 渕崎 員弘; 舩橋 達
Mater. Trans. JIM, 33(3), p.203 - 207, 1992/03
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:75.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)超音波パルスエコー法、X線及び中性子回折法を用いて、プレマルテンサイト相
 -Cu-27.0Al-5.5Pd合金の一軸応力下における格子振動の不安定性について調べた。(110)面間力についての非調和項が大きいために[001]一軸応力下での[110]TA
-Cu-27.0Al-5.5Pd合金の一軸応力下における格子振動の不安定性について調べた。(110)面間力についての非調和項が大きいために[001]一軸応力下での[110]TA フォノンエネルギーが極めて小さくなり、この振動モードの不安定性が増すことが判明した。この面間力解析によって[001]応力下で誘起されるマルテンサイト相は18R(又は9R)構造を持つと予想される。
フォノンエネルギーが極めて小さくなり、この振動モードの不安定性が増すことが判明した。この面間力解析によって[001]応力下で誘起されるマルテンサイト相は18R(又は9R)構造を持つと予想される。
星屋 泰二; 高田 文樹; 近江 正男; 後藤 一郎; 安藤 弘栄
日本金属学会誌, 56(5), p.502 - 508, 1992/00
二種類の照射温度(323及び520K)で最大速中性子フルエンス10 m
m まで中性子照射し、さらに照射後に523K以上の温度で焼鈍したTi-Ni系形状記憶合金の変態特性及び変形挙動を電気抵抗測定及び引張試験によって調べた。323Kで照射した場合、照射の影響は大きく、Ti-Ni系合金のM
まで中性子照射し、さらに照射後に523K以上の温度で焼鈍したTi-Ni系形状記憶合金の変態特性及び変形挙動を電気抵抗測定及び引張試験によって調べた。323Kで照射した場合、照射の影響は大きく、Ti-Ni系合金のM 温度は、10
温度は、10 dpa以上の損傷で急激に低下した。520Kで照射した場合、M
dpa以上の損傷で急激に低下した。520Kで照射した場合、M 温度低下は小さく、損傷の影響は極めて小さかった。Ti-Ni系形状記憶合金の照射下状態は二つの相反過程、すなわち不規則化と規則化からなる。この合金では、520K照射によって、空孔などの欠陥移動が熱振動で助長され、規則化が不規則化よりも優勢になるため、損傷回復現象が起こる。照射下の規則-不規則化理論を用いて、この現象を温度、損傷及び損傷率の関連から説明し、損傷回復現象が起こるしきい温度が520Kであることを明らかにした。
温度低下は小さく、損傷の影響は極めて小さかった。Ti-Ni系形状記憶合金の照射下状態は二つの相反過程、すなわち不規則化と規則化からなる。この合金では、520K照射によって、空孔などの欠陥移動が熱振動で助長され、規則化が不規則化よりも優勢になるため、損傷回復現象が起こる。照射下の規則-不規則化理論を用いて、この現象を温度、損傷及び損傷率の関連から説明し、損傷回復現象が起こるしきい温度が520Kであることを明らかにした。
星屋 泰二; 田昭 治*; 安藤 弘栄
日本金属学会誌, 56(7), p.741 - 746, 1992/00
中性子照射したTi-Ni系形状記憶合金の673K以下の温度における高温変形挙動さらには照射後に473,523,573Kで焼鈍した際の変形挙動を引張試験及び硬度試験を用いて調べた。中性子照射によって照射誘起超弾性など特異な変形挙動が生じた。これらは523K以上の温度における照射後焼鈍によって完全に回復した。この原因としては、照射によって生成した空孔などの欠陥移動が熱振動で助長され規則化過程を促進するためである。照射中のTi-Ni系形状記憶合金では、二つの相反する過程が競合して起きる。すなわち、照射誘起不規則と空孔移動によって促進される規則化である。これらの過程は照射温度と照射フルエンスに依存する。
星屋 泰二; 田昭 治*; 勝田 博司; 安藤 弘栄
日本金属学会誌, 56(7), p.747 - 756, 1992/00
低圧水素(1.1~78.5kPa)を吸収させたTi-50.5at.%Ni合金について、電気抵抗測定、引張試験、X線回折及び組織観察を行ない、Ti-Ni系合金の変態特性及び変形挙動に及ぼす水素の影響について調べた。電気抵抗測定及び引張試験結果から、この合金のM 温度は水素濃度とともに低下した。これは試料冷却過程のX線回折実験から判明した、水素による母相の安定化現象、すなわちマルテンサイト変態遅滞効果に対応する。すべり変形誘起応力は水素濃度とともに変化した。水素濃度が0.032mol%を越える場合は固溶体硬化現象(hardening)が、0.032mol%以下の場合は固溶体軟化現象(softening)が支配的であった。水素濃度が1.9mol%以上になると水素化物が形成した。これは組織観察において確認されたR相の兄弟晶の再配列や水素吸蔵後の母相格子の格子歪増加と関連する。
温度は水素濃度とともに低下した。これは試料冷却過程のX線回折実験から判明した、水素による母相の安定化現象、すなわちマルテンサイト変態遅滞効果に対応する。すべり変形誘起応力は水素濃度とともに変化した。水素濃度が0.032mol%を越える場合は固溶体硬化現象(hardening)が、0.032mol%以下の場合は固溶体軟化現象(softening)が支配的であった。水素濃度が1.9mol%以上になると水素化物が形成した。これは組織観察において確認されたR相の兄弟晶の再配列や水素吸蔵後の母相格子の格子歪増加と関連する。
星屋 泰二; 田昭 治*; 伊藤 治彦; 高村 三郎; 市橋 芳徳
日本金属学会誌, 55(10), p.1054 - 1062, 1991/10
中性子照射後(照射温度323K、速中性子照射フルエンス8 10
10 m
m )の等原子比TiNi系形状記憶合金の変態特性、変形挙動及び硬度特性を遠隔操作型の電気抵抗測定装置・引張試験装置・硬度試験装置を用いて調べた。その結果、TiNi系合金のマルテンサイト変態開始温度(M
)の等原子比TiNi系形状記憶合金の変態特性、変形挙動及び硬度特性を遠隔操作型の電気抵抗測定装置・引張試験装置・硬度試験装置を用いて調べた。その結果、TiNi系合金のマルテンサイト変態開始温度(M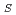 )は照射によって100K近傍まで低下し、その低下量は200K以上であった。一方、R相変態開始温度(T
)は照射によって100K近傍まで低下し、その低下量は200K以上であった。一方、R相変態開始温度(T )は照射前のそれと比較すると1Kから7K低温側に変化した。また、室温における破断応力及び破断歪(弾性歪を含む)は各々1300~1700MPa及び6~8%であった。さらに、引張試験において5%もの負荷歪が消失する特異な弾性挙動を見出した。TiNi系合金の中性子照射によって形成された原子変位は照射誘起不規則化を引き起こし、変態特性及び変形挙動に大きな影響を及ぼす。一方、523K、600s以上の照射後焼鈍によって規則化を促進して、損傷回復が起こる。
)は照射前のそれと比較すると1Kから7K低温側に変化した。また、室温における破断応力及び破断歪(弾性歪を含む)は各々1300~1700MPa及び6~8%であった。さらに、引張試験において5%もの負荷歪が消失する特異な弾性挙動を見出した。TiNi系合金の中性子照射によって形成された原子変位は照射誘起不規則化を引き起こし、変態特性及び変形挙動に大きな影響を及ぼす。一方、523K、600s以上の照射後焼鈍によって規則化を促進して、損傷回復が起こる。
 -like diffraction anomaly in the premartensitic
-like diffraction anomaly in the premartensitic 
 phase of AuCuZn
phase of AuCuZn alloy
alloy永澤 耿*; 喜田 和枝*; 森井 幸生; 渕崎 員弘; 片野 進; 舩橋 達; H.R.Child*
Mater. Trans. JIM, 32(11), p.1011 - 1016, 1991/00
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:47.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Heusler型結晶構造をもつ
 相AuCuZn
相AuCuZn 合金について(H
合金について(H 2/3,K
2/3,K 2/3,L
2/3,L 4/3)と(H
4/3)と(H 2/3,K
2/3,K 2/3,L
2/3,L 4/3)の逆格子点にあわられる
4/3)の逆格子点にあわられる ピーク状の回折ピークをX線と中性子を用いて調べた。このピークは不完全規則B
ピーク状の回折ピークをX線と中性子を用いて調べた。このピークは不完全規則B 相において、670KでHensler型規則構造へと変態する際の規則化を担う空孔が、ある種の規則配列をしたために起こることが判明した。この空孔は急冷処理によってHeusler型構造の中に凍結されると、
相において、670KでHensler型規則構造へと変態する際の規則化を担う空孔が、ある種の規則配列をしたために起こることが判明した。この空孔は急冷処理によってHeusler型構造の中に凍結されると、 ピーク状回折異常をもたらし、その後の昇温により空孔がなくなると、回折異常も消滅する。[111]LA、[112]TAフォノン分散関係の特徴も以上の結論を支持している。
ピーク状回折異常をもたらし、その後の昇温により空孔がなくなると、回折異常も消滅する。[111]LA、[112]TAフォノン分散関係の特徴も以上の結論を支持している。
 ders band propagation in a medium Mn steel
ders band propagation in a medium Mn steel小山 元道*; 山下 享介*; 諸岡 聡; Yang, Z.*; Varanasi, R.*; 北條 智彦*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
no journal, ,
The micro-deformation of an Fe-5Mn-0.1C medium Mn steel consisting of face-centered cubic and body-centered cubic phases was characterized through multi-scale in situ scanning electron microscopy. Specifically, multiscale in situ back-scatter electron imaging coupled with ex situ electron backscatter diffraction measurements was conducted under tensile testing. The Fe-Mn-C alloy showed macroscopically localized deformation (i.e., L ders deformation), and the deformation-localized region consisted of multiple find deformation bands. The hierarchical structure of the deformation bands initiated from a specimen side edge and propagated to the other side edge. More microscopically, the plastic deformation preferentially progressed in a face-centered cubic phase, and temporarily stopped when the fine deformation band encountered a group of body-centered cubic grains, which resulted in zigzag propagation of the fine deformation bands. Through coalescence of fine deformation bands, a thick macroscopic deformation band formed. By repetition of the micro-deformation process, the thick deformation band front moved along the tensile direction from an end of the gauge portion to the other end.
ders deformation), and the deformation-localized region consisted of multiple find deformation bands. The hierarchical structure of the deformation bands initiated from a specimen side edge and propagated to the other side edge. More microscopically, the plastic deformation preferentially progressed in a face-centered cubic phase, and temporarily stopped when the fine deformation band encountered a group of body-centered cubic grains, which resulted in zigzag propagation of the fine deformation bands. Through coalescence of fine deformation bands, a thick macroscopic deformation band formed. By repetition of the micro-deformation process, the thick deformation band front moved along the tensile direction from an end of the gauge portion to the other end.